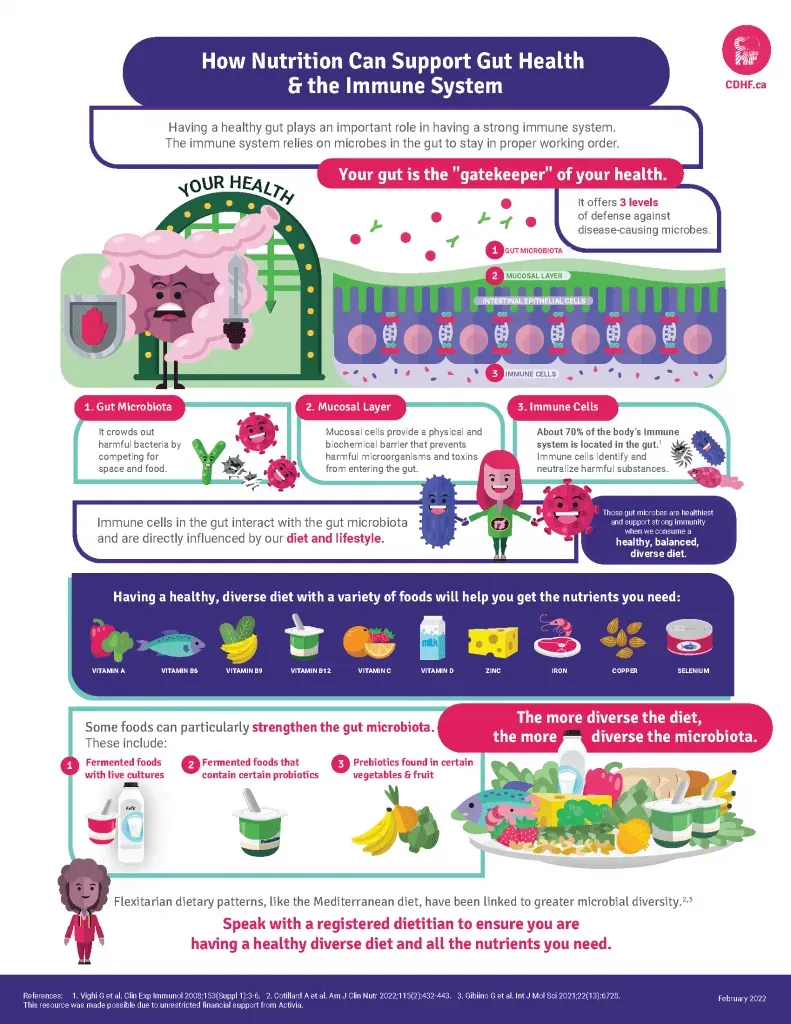
Gut Health and Immunity are deeply connected, shaping how we digest nutrients, absorb vitamins, and defend the body against everyday threats. By prioritizing gut health foods as part of a balanced day—think colorful vegetables, fermented staples, and whole grains—you can support steady energy and a more resilient immune response. Probiotics for immunity are a key piece, helping populate the gut with friendly bacteria and guiding immune signaling toward appropriate responses. When the microbiome thrives, the gut barrier strengthens, inflammation stays in check, and digestion can feel smoother even during periods of stress. This introductory guide lays out practical, tasty steps to nourish your gut while supporting immune health, with simple swaps and tasty meal ideas.
Beyond the phrase gut health and immunity, experts describe the same connection in terms of the intestinal microbiome and digestive-immune balance. A healthy microbial community in the digestive tract supports barrier integrity, reduces chronic inflammation, and helps the body’s defenses respond appropriately. Eating for microbial diversity—fiber-rich foods, fermented products, and plant-based nutrients—fosters a resilient immune system and steady nutrient uptake. Smart meal planning considers not just what to eat, but how these foods interact with gut lining, signaling pathways, and systemic wellness.
Gut Health and Immunity: Nourishing the Microbiome for a Stronger Immune System
Gut Health and Immunity are deeply connected. A thriving digestive system supports not only efficient nutrient absorption but also a robust immune response. When the gut microbiome is balanced with diverse beneficial bacteria, your body can fend off pathogens more effectively, respond to stresses, and maintain steady energy levels. The foods you choose every day—what we can call gut health foods—play a meaningful role in this dynamic, shaping barrier function and inflammatory tone. By focusing on probiotic-rich and fiber-forward options, you nurture a microbiome that trains immune cells to act appropriately and supports a healthier, more resilient immune system.
To optimize this connection, emphasize a mix of probiotics for immunity and prebiotic foods that feed those friendly microbes. Fiber for digestion fuels gut microbes to produce short-chain fatty acids that help regulate inflammation and strengthen the gut lining. Polyphenol-rich plant foods further support a diverse microbiome, enhancing the balance between gut health foods and immune-friendly responses. In practice, this means prioritizing yogurt or kefir, sauerkraut or kimchi, and a spectrum of leafy greens, legumes, whole grains, and colorful produce to sustain both digestion and immunity.
Immune-Boosting Foods: Practical Strategies to Support Digestion and Defense
A practical approach to immune-boosting foods centers on four pillars: probiotics, prebiotic foods, fiber, and polyphenols. This combination fosters a hospitable gut environment while delivering nutrients that support immune cells. By integrating foods rich in probiotics for immunity—such as fermented dairy or beet-rich kefir—and pairing them with prebiotic foods like garlic, onions, and leeks, you can fuel a thriving microbial community that bolsters defense against illness. This strategy also aligns with fiber for digestion, ensuring steady transit, balanced blood sugar, and a steady supply of nourishment for beneficial bacteria.
Craft a simple weekly plan that highlights gut health foods and immune-supporting options. Start each day with a probiotic-rich breakfast, like yogurt or kefir with berries and oats, then build meals around fiber-forward grains, legumes, and an abundance of vegetables. Include prebiotic choices at lunch or dinner, such as garlic-tueled sauces or onion-forward salads, and finish with polyphenol-rich desserts or beverages like berries or green tea. By intentionally rotating fermented foods, high-fiber ingredients, and omega-3 sources, you create a sustainable pattern of immune-boosting foods that also promote healthy digestion.
Frequently Asked Questions
How do gut health foods support immunity and digestion?
Gut health foods help balance the gut microbiome, supporting barrier function and immune signaling. Probiotics for immunity (live cultures found in yogurt, kefir, and fermented foods) can populate the gut with friendly bacteria, while prebiotic foods (garlic, onions, leeks, asparagus, bananas) feed them. fiber for digestion fuels gut microbes and promotes short-chain fatty acids that modulate inflammation and strengthen immunity. Together, these components create a resilient gut-immune axis and a robust response to stressors.
What are simple daily meals that boost gut health and immunity using immune-boosting foods and prebiotic fiber?
Aim to include probiotic and prebiotic elements at each meal. For example: Breakfast with yogurt or kefir and berries; Lunch a colorful salad with leafy greens, beans or lentils, and a side of sauerkraut; Dinner a salmon fillet with roasted vegetables and quinoa; Snacks like an apple with almond butter. Add garlic or onions to sauces for extra prebiotic foods, and stay hydrated with green tea or water to support digestion. These patterns leverage gut health foods to support immunity while keeping fiber for digestion front and center.
| Topic | Key Points |
|---|---|
| Introduction | Gut Health and Immunity are deeply connected; a thriving digestive system supports nutrient absorption and immune response; a balanced gut microbiome enables better defense, stress response, and steady energy; daily food choices impact digestion and immunity. |
| Gut-immune connection | The gut houses much of the immune system and acts as a communication hub between diet, microbiome, and immune cells; a healthy microbiome trains immune cells; dysbiosis increases inflammation and infection risk; a balanced microbiome supports barrier function and resilience. |
| Four pillars | Probiotics, Prebiotics, Fiber, and Polyphenols are the main dietary pillars; probiotics are live bacteria; prebiotics feed them; fiber fuels microbes and helps regulate inflammation; polyphenols are antioxidants that promote a diverse microbiota. |
| Top foods categories | Fermented foods (probiotics); High-fiber foods; Prebiotic-rich foods; Polyphenol-rich foods; Omega-3 fatty acids; Vitamin/mineral-dense foods; Hydration and mindful eating practices. |
| Weekly plan concept | Design meals around probiotics, prebiotics, fiber, and polyphenols with balanced macronutrients; includes practical meal ideas for breakfast, lunch, dinner, snacks, and beverages. |
| Lifestyle habits | Regular physical activity, adequate sleep, and stress management are vital; exercise supports microbiome diversity and immune function; sleep loss can disrupt gut barrier; mindfulness and breathing support digestion. |
| Common pitfalls | Avoid ultra-processed foods and added sugars; limit unnecessary antibiotics; balance probiotics and prebiotics with fiber; stay hydrated; introduce dietary changes gradually. |
| Myths vs truths | Myths and truths include: probiotics alone aren’t enough for gut health; healthy fats (especially omega-3s) can help inflammation; gluten-free isn’t inherently gut-healthy; focus on a diverse, fiber-rich diet. |
| Two-week plan | Week 1 emphasizes consistent probiotic and prebiotic intake with diverse fiber; Week 2 adds more polyphenol-rich foods and omega-3 sources; gradually increase fiber to avoid discomfort. |
Summary
Table summarized above highlights the key points about Gut Health and Immunity from the base content.