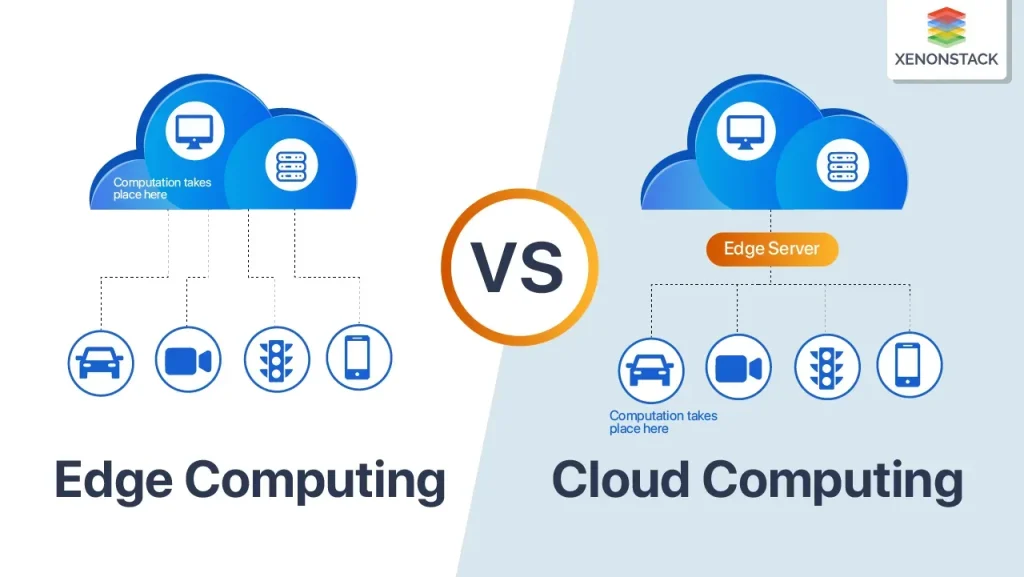
Edge Technology vs Cloud is reshaping how organizations decide where to run workloads, store data, and deploy intelligence. Understanding edge computing advantages helps teams reduce latency, ease bandwidth pressure, and unlock real-time insights at the data source. Latency reduction in edge computing makes critical applications like industrial control and remote monitoring more responsive. Security in edge computing requires distributed defenses, secure boot, and strong authentication to protect numerous edge devices. A hybrid edge cloud strategy often delivers the right balance, combining edge speed with cloud scalability for resilient architectures.
Seen through the lens of on-device processing, the choice becomes a spectrum rather than a single winner. In this frame, near-edge computing, local data processing, and gateway-level analytics describe the same trend as edge technology, while centralized cloud resources enable scalable AI, governance, and data consolidation. By aligning capabilities to latency, data sovereignty, and cost, organizations can allocate workloads across the edge and the cloud for optimal performance. This LSI-informed approach uses related concepts like edge analytics, distributed computing, and scalable storage to guide architecture decisions.
Edge Technology vs Cloud: Why a Hybrid Edge Cloud Strategy Delivers Speed, Security, and Scale
The choice between edge technology and cloud computing isn’t a zero-sum decision. A hybrid edge cloud strategy blends the strengths of both to unlock speed, resilience, and scalable analytics. When we talk about edge computing advantages, ultra-low latency, bandwidth savings, and the ability to operate in environments with intermittent connectivity stand out as key benefits. A primary objective in many architectures is latency reduction in edge computing, ensuring real-time responses for time-critical tasks while still leveraging centralized resources when appropriate.
Security in edge computing becomes a distributed, defense-in-depth challenge, but cloud environments offer centralized controls, comprehensive monitoring, and mature identity management. By aligning edge and cloud with a cohesive security model, organizations can achieve robust protection across devices and data stores. This is where the hybrid edge cloud strategy shines: you get the flexibility to deploy resources where they matter most while retaining the governance, compliance, and cloud computing benefits that underpin enterprise security and reliability.
Edge vs Cloud for Data Processing: Choosing the Right Balance with a Hybrid Edge Cloud Strategy
Allocating workloads by latency sensitivity is fundamental to effective edge vs cloud for data processing decisions. Edge processing excels at immediate inference, local filtering, and real-time monitoring, delivering latency reduction in edge computing that preserves user experience and system stability. In many scenarios, edge computing advantages translate to faster decision cycles and reduced network dependency, enabling more predictable performance for critical applications.
For heavier analytics, centralized data governance, and scalable machine learning, cloud computing benefits are compelling. A hybrid edge cloud strategy coordinates data flows so edge devices handle quick, local tasks while the cloud aggregates, analyzes, and orchestrates across sites. This approach leverages cloud computing benefits like elastic compute, global data access, and robust data management, while maintaining the edge’s responsiveness and resilience for data processing at the source.
Frequently Asked Questions
Edge Technology vs Cloud: How do you decide when to prioritize edge computing advantages vs cloud computing benefits for data processing?
Edge computing advantages include ultra-low latency, real-time decision-making, bandwidth savings, and operation in environments with intermittent connectivity. Cloud computing benefits offer scalable compute and storage, global availability, and a rich ecosystem of managed analytics and AI services. For data processing, choose edge when latency, local data locality, or offline operation matters; choose cloud when you need heavy analytics, large-scale data processing, or centralized governance. In practice, many organizations adopt a hybrid edge cloud strategy that pushes latency-sensitive tasks to the edge while sending summarized data to the cloud for deeper analytics and orchestration.
Edge Technology vs Cloud: How does a hybrid edge cloud strategy balance latency reduction in edge computing and security in edge computing while leveraging cloud advantages?
A hybrid edge cloud strategy distributes workloads based on latency, data sensitivity, and governance. Use the edge to handle latency reduction in edge computing for real-time monitoring, control, and pre-processing, while the cloud handles long-running analytics, model training, and centralized data publication. Security in edge computing should be addressed with device hardening, encryption, authentication, and zero-trust across both environments, while cloud security relies on centralized IAM, monitoring, and compliant data handling. Data governance, data flow design, and consistent security policies across edge and cloud are essential. This approach delivers the Edge Technology vs Cloud balance by applying each paradigm where it shines: speed at the edge and scale in the cloud.
| Topic | Key Points |
|---|---|
| What are Edge Technology and Cloud? | Edge processes data close to data sources; Cloud provides centralized compute, storage, and services; they complement each other. |
| Core Strengths | Edge: ultra-low latency, bandwidth savings, operation with intermittent connectivity; Cloud: massive processing, elasticity, global reach, rich service ecosystems. |
| When Edge Shines vs When Cloud Wins | Edge for real-time control and latency-sensitive tasks (e.g., manufacturing, autonomous devices); Cloud for heavy analytics, long-running processing, centralized data access. |
| Architectural Patterns | Edge-first, Cloud-first, or Hybrid edge-cloud strategy that assigns workloads to the best location with orchestrated data flow. |
| Hybrid Edge-Cloud Strategy | Blend edges for latency-sensitive tasks with Cloud for scale, governance, and deeper analytics; requires clear data flows and governance. |
| Security & Compliance | Edge demands distributed security controls and device hardening; Cloud enables centralized security, IAM, and monitoring; harmonize policies across environments. |
| Latency & Data Processing | Edge reduces round-trip time for immediate actions; Cloud processes large datasets and derives insights at scale; use hybrid to balance latency and analytics. |
| Cost & ROI | Edge involves upfront device/gateway costs; Cloud adds ongoing storage and usage costs; Hybrid can lower data movement and optimize bandwidth for cost efficiency. |
| Implementation Roadmap | Define business goals, classify workloads by latency, design data flows, choose interoperable infrastructure, enforce security, establish governance, and pilot before scaling. |
| Real-World Scenarios | Scenario A: Edge on shop floor with cloud for cross-site analytics; Scenario B: Edge gateways for stores with cloud data lake; Scenario C: Edge for patient monitoring with cloud analytics. |
Summary
Conclusion: Edge Technology vs Cloud is not a binary choice; it is a coordinated architecture that blends speed, scale, and resilience. By embracing a hybrid edge-cloud approach, organizations can achieve ultra-low latency for time-critical tasks, scalable analytics for strategic insights, and robust governance across environments. Edge Technology vs Cloud should be viewed as complementary capabilities that, when aligned to business goals and data governance, unlock faster decision-making, better user experiences, and a stronger competitive position.